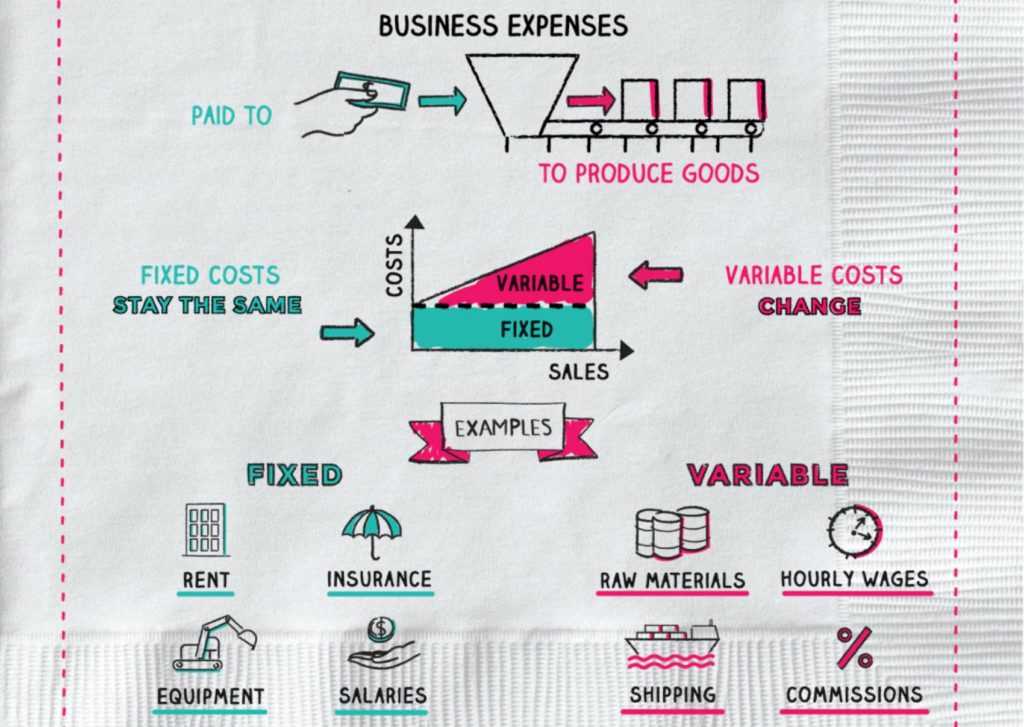
Understanding the behaviour of costs as the trading patterns in a business change is an area of vital importance to decision makers. To be able to control costs and to see how they behave under changing conditions first it is essential to identify the different types of cost.
Fixed costs
Fixed costs are costs that do not vary with the level of activity, the level of output, in the short term.
Examples of fixed costs
- Rent
- Labour
- Equipment
- Computers
- Advertising
- Insurance
- Depreciation
Fixed costs in the short term can be represented on a graph, as follows:
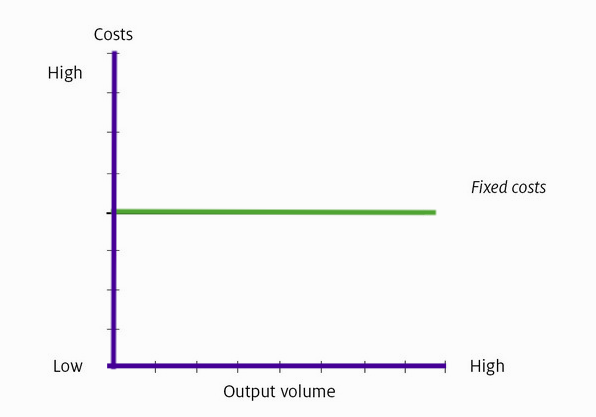
When a business has reached a satisfactory sales and profit level, the management can decide to extend the activity and for example open another plant. That decision may involve additional costs as rent, equipment, labor etc. and the fixed costs graph can be represented as follows:
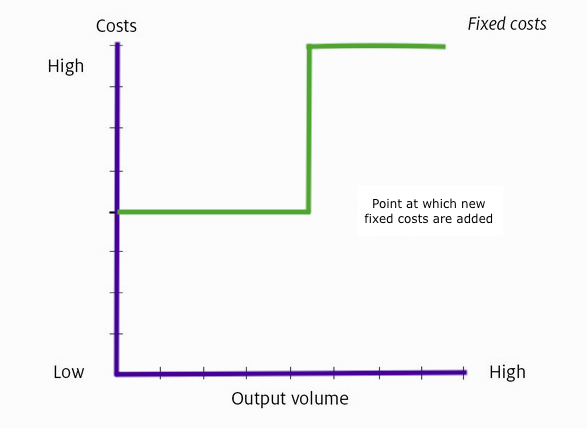
These costs are fixed with respect to short-term changes in the level of output only. In the long-term, fixed costs are likely to change.
Variable costs
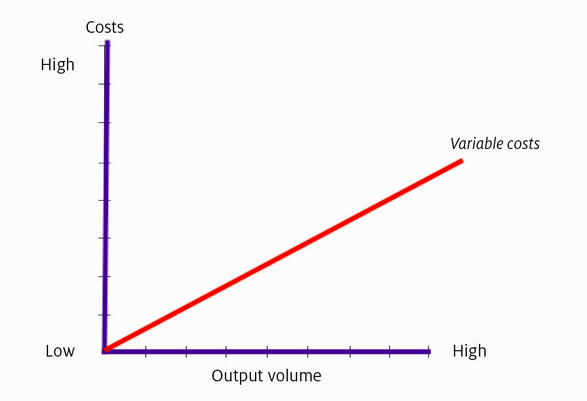
Variable costs are costs that vary in direct proportion with the level of activity.
These are costs that change in line with output. Variable costs are the sum of marginal costs over all units produced. Variable costs are sometimes called unit-level costs as they vary with the number of units produced.
Examples of variable costs
- Raw materials for production
- Packaging materials
- Bonuses
- Sales commission
- Hourly wages
- Shipping
Semi-variable costs
Semi-variable costs are costs that unfortunately cannot fit easily into either the fixed or variable category. A semi-variable cost is an expense, which includes a mixture of fixed and variable components.
The fixed cost element is the part of the cost that must be paid irrespective of the level of activity. On the other hand the variable component of the cost is payable proportionate to the level of activity. These costs are sometimes called mixed costs. In some cases, costs may be fixed for a set level of production, becoming variable after that level is exceeded (e.g. telephone bills).
Total costs
Total costs are the sum of fixed costs, semi-variable costs and variable costs for any particular level of output. If the output level is zero, then total costs would consist only of fixed costs.
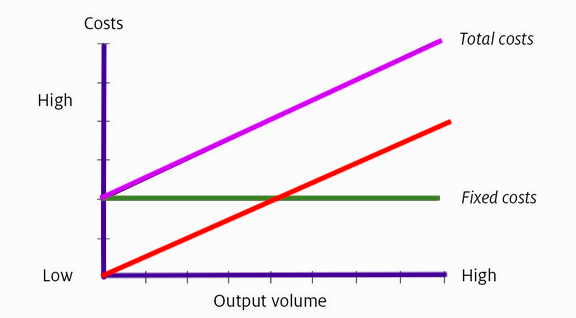
Taking vertical and horizontal lines from any point in the total cost line will give the total costs for any chosen output volume. This is an essential feature of the costing model that lets us see how costs change with different output volumes: in other words, accommodating the dynamic nature of a business.